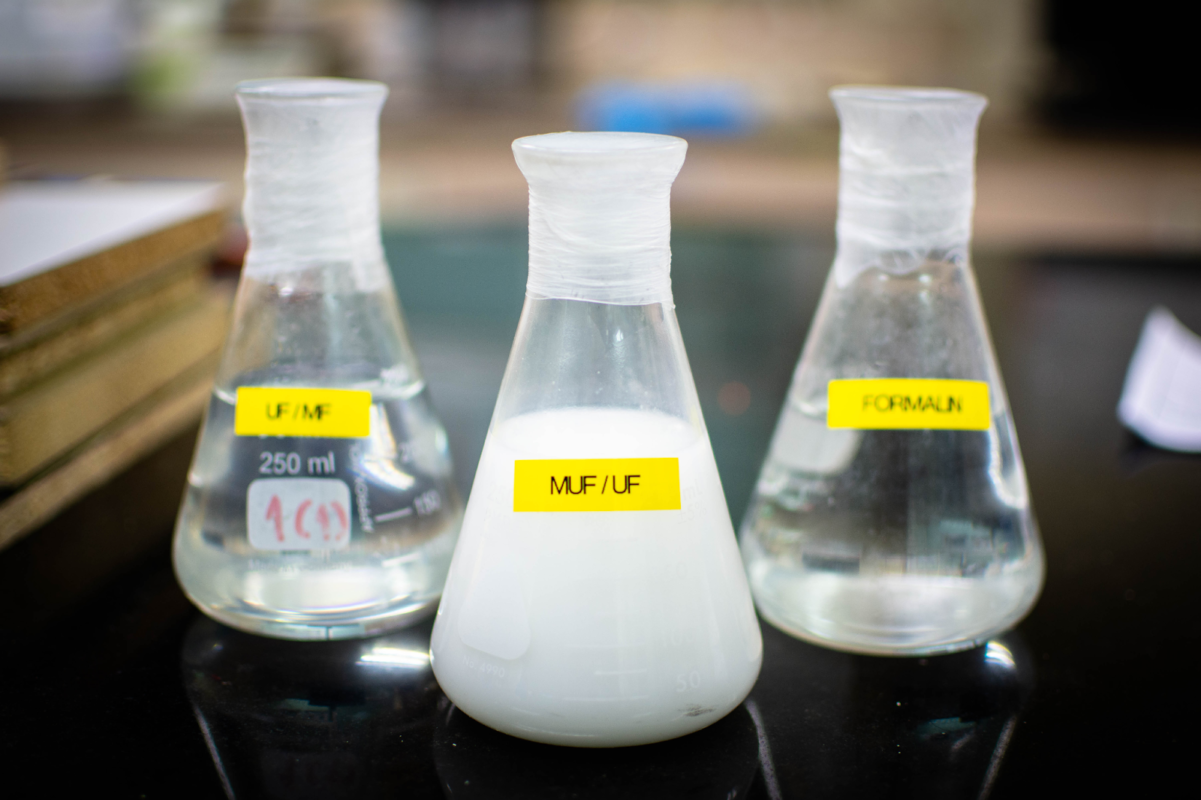
In plywood production, the choice of glue plays a pivotal role in determining the performance, durability, and environmental characteristics of the final product. Different types of glue, such as urea-formaldehyde, phenol-formaldehyde, and melamine-formaldehyde, each offers unique advantages and considerations. This article will analyze the characteristics of the three most popular types of glue in Vietnam plywood production.
1. Urea Formaldehyde Glue (UF)
UF Glue is widely utilized in plywood production, offering cost-effectiveness and durability suitable for various applications. This glue is composed of urea and formaldehyde, with different formulations catering to specific requirements.
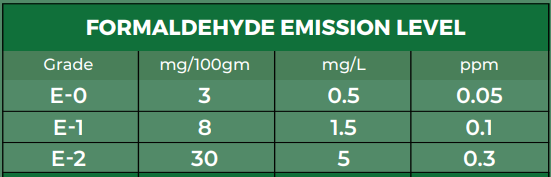
E0, E1, E2 Grades: Different governments regulate these grades to indicate varying levels of formaldehyde emissions. Manufacturers commonly use E0 and E1 glues in indoor furniture due to their low formaldehyde emissions, which comply with stringent environmental standards and ensure good indoor air quality. UF E2 glue offers a more economical option for applications with less stringent formaldehyde regulations or higher cost considerations. This glue is often used in outdoor furniture production and construction projects where moisture resistance requirements are lower.
(Image: Formaldehyde emission level)
Advantages:
- Lower cost: UF glue is generally more affordable compared to other glue types used in plywood manufacturing, making it a preferred choice for budget-sensitive projects.
- Relatively short pressing time: UF glue typically requires shorter pressing times during plywood production, which can improve manufacturing efficiency and reduce production costs.
Disadvantages:
- Poor water resistance: UF glue does not offer strong water resistance properties, making plywood bonded with UF glue susceptible to degradation when exposed to moisture over time.
- Lack of moisture resistance for laminated boards: Plywood bonded with UF glue may not withstand prolonged exposure to moisture or humid conditions, limiting its suitability for exterior applications or areas prone to high humidity levels.
In Vietnam, plywood producers commonly use UF E2 glue and mixed water glue variants, especially in applications with less stringent requirements for formaldehyde emission and moisture resistance. This choice reflects a balance between cost-effectiveness and performance suitable for specific environmental conditions and application needs in the local market.
2. Melamine-Urea-Formaldehyde Glue (MUF)
MUF Glue combines melamine, urea, and formaldehyde to achieve a robust glue known for its durability and heat resistance. This type of glue particularly suits applications that require high durability and resistance to water and heat, such as in producing film-faced plywood.
Variants (E0 to E2): MUF glue is available in different grades ranging from E0 to E2, which denote varying levels of formaldehyde emissions regulated by different standards. These grades cater to both domestic manufacturing needs and export requirements.
Melamine Content: The characteristics of MUF glue depend on the percentage of melamine incorporated into the glue. Higher percentages of melamine enhance the water resistance of the plywood. The maximum water resistance level for MUF-glued plywood is typically around 72 hours of boiling, making it suitable for outdoor furniture and products requiring robust moisture resistance, such as marine plywood, film-faced plywood, and laminated veneer lumber.
Advantages:
- Good water resistance: MUF glue offers superior water resistance compared to UF glue types, making it suitable for applications exposed to moisture or outdoor conditions.
- Relatively good mechanical strength: The glue strength of MUF glue helps prevent delamination, ensuring the integrity and longevity of the plywood.
- Suitable for various applications: It is versatile and used in a range of products requiring durability and moisture resistance, such as marine-grade plywood and structural panels.
Disadvantages:
- Moisture content limitations: MUF glue cannot be used effectively when the moisture content of the core veneer is high. Proper veneer drying is essential to ensure effective bonding.
- Higher cost: Compared to UF glues, MUF glue tends to be more expensive due to the inclusion of melamine and its enhanced performance characteristics.
3. Phenol-Formaldehyde Glue (PF)
PF Glue is manufactured from phenol and formaldehyde, offering superior heat resistance and pressure resistance compared to other types of glues. This characteristic makes PF glue particularly suitable for applications requiring exceptional durability and adhesion.
PF glue offers high heat resistance, enabling plywood and other wood products bonded with this glue to endure prolonged exposure to high temperatures. Plywood made with PF glue can typically endure boiling for over 72 hours without delaminating or separating layers, making it ideal for applications where heat resistance is critical.

Manufacturers primarily use PF glue in the production of construction plywood, where durability and strength are paramount. PF is also a good choice for manufacturing water-resistant and heat-resistant medium-density fiberboard (MDF) boards, contributing to their stability and performance in demanding environments.
Advantages:
- Extremely high mechanical strength: PF glue provides exceptional bonding strength, enhancing the structural integrity and longevity of wood products.
- Excellent water resistance: Plywood bonded with PF glue exhibits excellent resistance to water and moisture, making it suitable for exterior and marine applications.
- High heat resistance: The glue’s ability to withstand high temperatures ensures the durability and reliability of wood products under challenging conditions.
Disadvantages:
- Limited availability of raw materials: Phenol, a key raw material for PF glue, may have limited availability or higher costs in certain regions, affecting production feasibility.
- Higher cost: PF glue tends to be more expensive in comparison with other glue types due to its specialized formulation and performance characteristics.
- High formaldehyde emission: PF glue can emit higher levels of formaldehyde compared to other glues, requiring careful management and compliance with regulatory standards to minimize environmental impact and ensure indoor air quality.
In conclusion
Choosing the appropriate glue type depends on several factors, including the intended use of the plywood, environmental conditions, and regulatory requirements. Manufacturers must balance cost considerations with performance requirements to produce plywood that meets industry standards and customer expectations.
Understanding the properties and characteristics of each glue type enables manufacturers to optimize their production processes. By selecting the right glue, they can enhance the structural integrity, moisture resistance, and overall quality of plywood, ensuring it meets the diverse needs of construction, furniture manufacturing, and other industrial applications. This informed decision-making not only improves the product’s performance but also contributes to sustainable practices by reducing material waste and enhancing product longevity.