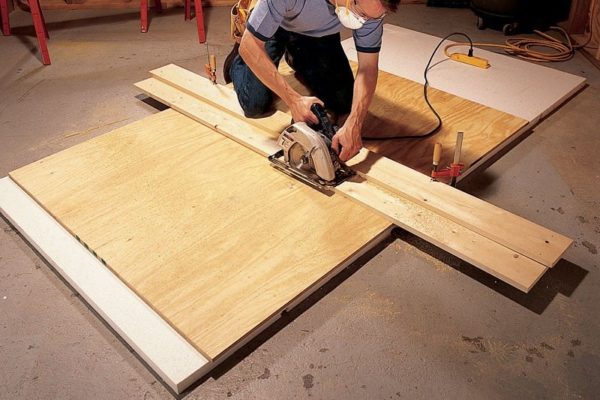
The choice between blockboard and plywood depends on the project. If you want a smooth finished surface and the durability of the board is not a primary factor, then blockboard is a good choice. However, if strength is more important, plywood is the better option. For instance, plywood can be used for subflooring under tiles and engineered hardwood, whereas blockboard is not suitable and will be crushed underfoot.
1. Material
Plywood
Plywood is a wooden panel made by stacking and gluing wood veneer sheets which are then pressed under high temperature to form sheets. It is used for interior purposes such as flooring and making furniture, as well as for exterior purposes like roofing.
Blockboard
Blockboard is wood based board which consists of a core made of softwood wood strips between the two layers of wood veneers. The strips are placed of edge to edge and are enclosed between hardwood veneer sheets and glued under high temperature and pressure.
2. Uses
Plywood:
- Use plywood to create custom-built furniture for homes and offices, but avoid it for long-span furniture due to its tendency to sag or bend in the middle.
- Employ plywood in building construction for concrete formwork panels, flooring, walls, and roofing.
- Choose BWR grade plywood, known for its waterproof properties, for making kitchen cabinets and other kitchen furniture.
- Build fences and signs for outdoor advertising with plywood to ensure durability in challenging environments.
- Utilize marine-grade plywood for constructing boats and ships.
- Extend plywood’s use to DIY projects for home improvement and crafting.
Blockboard:
- Choose blockboard for furniture requiring long pieces of wood, such as long bookshelves, tables, benches, wall panels, wardrobes, doors, and sliding panels, because blockboard remains stiff and does not bend or sag like plywood.
- Opt for blockboard due to its lightweight nature, which simplifies transportation and installation, making it the top choice for both exterior and interior doors.
3. Properties
3.1 Resistance to Physical Components
| Plywood | Blockboard | |
| Water |
|
|
| Sagging and Bending |
|
|
| Warping and Cracking |
|
|
3.2 Uniformity
- Plywood: is uniform throughout its length and breadth.
- Blockboard: has minor gaps between the blocks which cannot be seen from outside.
3.3 Weight
- Plywood: is heavier than blockboard as its core is made of hardwood veneer, which is quite dense and solid.
- Blockboard: is light in weight than plywood because its core is made from softwood whose density and weight is less than that of hardwood.
3.4 Cutting
- Plywood: is a little difficult to cut as compared to blockboard and will also splinter badly when cut.
- Blockboard: is easy to work with and can be cut using regular wood work tools.
3.5 Fitting
- Plywood: can hold screws and nails very well.
- Blockboard: also has very good screw holding capacity like plywood but, often because of the gaps in between the blocks, the nails can sometimes go into the gaps instead of the wood and hence need skilled workers.
3.6 Surface Finishing
- Plywood: can be easily painted, laminated, veneered or lacquered.
- Blockboard: is available with various finishes such as plastic laminates, wood veneers, melamine paper, etc. It can also be painted and polished.
3.7 Strength and Durability
- Plywood: has high strength as well as durability owning to its cross laminated structure.
- Blockboard: As it is made using softwood, it is not as strong as hardwood plywood. But, if hardwood strips are used, the strength of block board can be increased.
4. Maintenance
- Use a dry dusting cloth to remove dust and dirt.
- Do not let spills to stay on the surface and immediately clean it with a dry cloth.
- Use clean soft and dry cloth to remove dust.
- Do not wipe it with wet mop and make sure it stays away from water.
5. Life span
- Plywood remains durable over an extended period if kept dry. When laminated or veneered, it can last up to 50 years. In a dry environment, its lifespan can be further extended by several additional years. Regular maintenance and proper sealing can also enhance its longevity and performance.
- Blockboard has a shorter lifespan compared to plywood. However, among engineered wood products, it is recognized for its superior strength and durability.
6. Cost
- Plywood tends to be more expensive than blockboard. However, its higher cost is often justified by its greater durability and versatility, which can result in long-term savings and better performance for various applications. Investing in plywood can also enhance the overall quality and lifespan of the finished product.
- Blockboard is more affordable than plywood because it uses softwood strips for its core. This cost-effectiveness makes it a popular choice for budget-conscious projects.
In conclusion
Select between plywood and blockboard based on the specific application and your budget constraints. Plywood is highly recommended for custom-made furniture that needs to bear heavy loads, such as large cabinets and kitchen fixtures, due to its superior strength and durability. It is also an excellent choice for high-stress applications because of its resistance to bending and sagging. On the other hand, blockboard is well-suited for furniture items such as shelves, tables, and benches, where its lighter weight and ease of handling are advantageous.